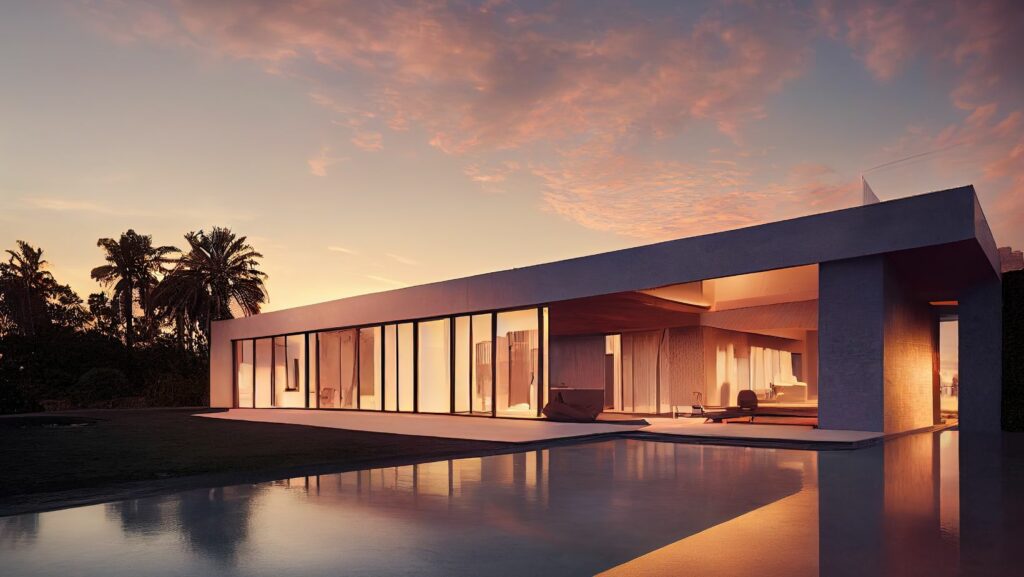
In the heart of Colorado, Vail architects are setting a benchmark in sustainable residential design, reflecting a broader trend in the architecture industry where sustainability is no longer an option but a necessity. As environmental concerns continue to shape public consciousness, residential architects across the globe are increasingly focusing on incorporating sustainable practices into modern home designs. This shift not only meets the growing demand for eco-friendly living spaces but also plays a crucial role in mitigating the environmental impact of construction and habitation.
The Rise of Sustainable Residential Architecture
Sustainability in architecture goes beyond just using green materials; it’s about creating homes that are energy-efficient, environmentally responsible, and capable of supporting a healthier lifestyle. The rise of sustainable residential architecture is driven by several factors, including stricter building codes, increased awareness of climate change, and a growing market for eco-friendly homes. Today’s homeowners are more informed and concerned about their carbon footprint, leading to a demand for homes that minimize environmental impact while maximizing comfort and efficiency.
Residential architects are responding by designing homes that are not only beautiful and functional but also sustainable. This holistic approach to design ensures that every aspect of a home—from its construction materials to its energy systems—contributes to a sustainable future.
Energy Efficiency: The Cornerstone of Sustainable Homes
Energy efficiency is a key component of sustainable home design. Residential architects are increasingly incorporating features that reduce energy consumption, such as high-performance insulation, energy-efficient windows, and advanced HVAC systems. These elements help maintain comfortable indoor temperatures with minimal energy use, reducing both the environmental impact and utility costs for homeowners.
Passive solar design is another strategy employed by architects to enhance energy efficiency. By orienting homes to maximize natural light and heat from the sun, architects can reduce the need for artificial lighting and heating. This design approach not only lowers energy bills but also creates a more comfortable and inviting living environment.
In addition to passive solar design, architects are integrating renewable energy sources such as solar panels and wind turbines into residential designs. These systems allow homeowners to generate their own clean energy, further reducing their reliance on non-renewable energy sources and minimizing their carbon footprint.
Sustainable Materials: Building Homes with a Smaller Footprint
The choice of materials is crucial in sustainable home design. Residential architects are increasingly opting for materials that are locally sourced, recycled, or have a low environmental impact. For example, bamboo, reclaimed wood, and recycled steel are popular choices for their sustainability and durability.
Incorporating sustainable materials into home design not only reduces the environmental impact of construction but also promotes healthier indoor environments. Many traditional building materials contain harmful chemicals that can off-gas into the home, affecting indoor air quality. By using natural, non-toxic materials, architects can create healthier living spaces that benefit both the environment and the occupants.
Moreover, sustainable materials often contribute to the longevity and resilience of a home. For instance, materials like reclaimed wood and recycled steel are not only environmentally friendly but also highly durable, ensuring that the home remains structurally sound for decades to come. This long-term durability is a key aspect of sustainability, as it reduces the need for frequent repairs and replacements, further minimizing environmental impact.
Water Conservation: Designing for Efficiency
Water conservation is another critical aspect of sustainable home design. Architects are increasingly incorporating systems and features that minimize water usage, such as low-flow fixtures, rainwater harvesting systems, and drought-resistant landscaping. These elements are particularly important in regions where water scarcity is a concern.
Greywater recycling systems, which reuse water from sinks, showers, and laundry for irrigation or toilet flushing, are becoming more common in sustainable residential designs. These systems significantly reduce the demand for freshwater, helping to conserve this vital resource.
Additionally, sustainable landscape design plays a crucial role in water conservation. By choosing native and drought-resistant plants, architects can create beautiful, low-maintenance gardens that require minimal watering. This approach not only conserves water but also supports local ecosystems by providing habitats for native wildlife.
Indoor Environmental Quality: Creating Healthy Living Spaces
A key goal of sustainable residential architecture is to create homes that support the health and well-being of their occupants. This involves designing for optimal indoor environmental quality, which includes factors such as air quality, lighting, and acoustics.
Architects are incorporating features that improve indoor air quality, such as ventilation systems that filter pollutants and humidity control systems that prevent mold growth. The use of non-toxic materials and finishes also contributes to healthier indoor environments by reducing the presence of harmful chemicals.
Natural lighting is another important consideration in sustainable home design. By maximizing the use of daylight through strategic window placement and the use of skylights, architects can create bright, welcoming interiors that reduce the need for artificial lighting. This not only conserves energy but also has been shown to have positive effects on mental and physical health.
Acoustic design is also becoming a focus in sustainable architecture. By incorporating sound-absorbing materials and designing layouts that minimize noise pollution, architects can create peaceful, serene living environments that enhance the overall quality of life for residents.
The Future of Sustainable Residential Architecture
As the demand for sustainable homes continues to grow, residential architects are at the forefront of this important movement. The principles of sustainability are being integrated into every aspect of home design, from energy efficiency and material selection to water conservation and indoor environmental quality.
Looking ahead, the future of sustainable residential architecture will likely see even greater innovation as architects continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible. New technologies, materials, and design strategies will emerge, further enhancing the sustainability and livability of modern homes.
For homeowners and architects alike, the commitment to sustainability is not just about meeting today’s needs but also about preserving the planet for future generations. By designing homes with purpose and intention, architects are helping to create a more sustainable, healthier, and resilient world.



More Stories
Predictive Betting Models Used by Aussie Gamblers: Advanced Approaches to Wagering in 2025
What Should You Look for When Purchasing a Premium Men’s Linen Shirt?
The Casino Experience: Types, Appeal, Rules & Online Vs. Offline Debate